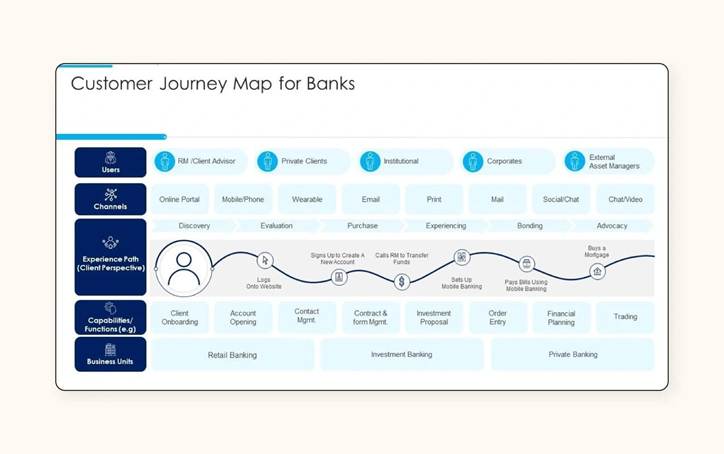
Customer journey visualization can boost retention by up to 15% in six months. This fact surprises many business owners.
Companies that map and understand their customers’ paths learn valuable lessons that lead to measurable outcomes. Our experience shows how visualizing customer trips helps spot major issues and uncovers new ways to enhance user experience. Visual customer journey maps can speed up your sales process and increase your conversion rates.
A well-designed customer trip map becomes a powerful tool that combines product analytics, primary research, and customer interactions. This complete view shows all touchpoints and lets you monitor how potential customers move through each stage of your sales funnel.
Let’s look at a simple example: if 1,000 people visit your website but only 300 download your product catalog, you can quickly see where to focus your improvements.
This piece offers step-by-step instructions to create journey maps that deliver business results. We provide practical advice to help you reduce churn, find upselling opportunities, and improve your product strategy.
Understand the Purpose of Customer Journey Visualization
Customer trip visualization shows how customers interact with your brand at every point of contact. This visual mapping does more than create simple flowcharts. It paints a detailed picture of the entire customer experience – from the first time they hear about you through their ongoing relationship after purchase.
Why mapping the customer trip matters
Visualizing customer trips creates discussions and builds a shared mental model throughout your organization. This shared understanding is vital because often splits up within companies. No single department sees the complete experience from the customer’s view. Trip maps connect these departmental silos with a visual tool that shows customer needs to everyone.customer experience
Customer trip mapping helps you:
- Identify pain points and opportunities in the customer experience that all stakeholders can see right away
- Predict customer behavior and know what they’ll need before they ask
- Make use of information to guide product development and marketing plans
- Arrange your whole business around what customers actually experience rather than what you think they want
The business value stands out—80% of today’s companies compete mainly on customer experience. Brands that give excellent customer experiences can boost revenue by 2-7%. These numbers show the direct link between trip visualization and business results.
Trip mapping changes the focus from company thinking to accessible design. You see exactly what customers experience at each step instead of building experiences on assumptions. This approach shows gaps and inconsistencies you might miss otherwise.
How it improves user experience and retention
Trip visualization makes both user experience and retention better by finding moments of frustration and delight in all customer interactions. This detailed view lets you:
You can spot specific friction points that slow down or stop conversions. This helps you fix problems before customers give up. To cite an instance, seeing the customer path might show that people get confused during checkout or can’t find help easily—problems you can fix once you know about them.
The experience stays consistent across all contact points. Customer trips often use many channels, from social media to website visits to email messages. This mapping gives you one clear view of how customers use these channels. Your message and experience stay the same everywhere.
Retention results really matter. Research shows that keeping just 5% more can increase profits up to 95%. This proves why trip visualization helps sustainable growth. The numbers also show that 94% of customers buy again after a good experience. When you map and improve each stage of the trip, you create more of these positive moments that build lasting loyalty.customer retention rates
Trip visualization also creates chances for personal touches throughout the customer’s time with you. You can make your messages and offers more relevant by understanding what drives customers at different points. This targeted approach builds trust and creates stronger emotional bonds with your brand.
Trip mapping helps you keep getting better. Customer expectations change over time, so your visualizations should change too. This ongoing improvement keeps your customer experience fresh and competitive, leading to satisfied and loyal customers.
Trip visualization turns complex customer information into clear action steps. Instead of getting lost in scattered numbers, you get a clear picture of how each interaction adds to the overall experience—and exactly where improvements will help both satisfaction and profits the most.
Define Clear Goals and Scope
You need to set proper boundaries and direction before you start creating your visual customer journey map. Your journey mapping success depends on clear parameters that give your work purpose and focus.
Set measurable objectives
The foundation of effective journey visualization starts with concrete, measurable goals that line up with your broader business objectives. Your mapping project should follow SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This well-laid-out approach will give your journey mapping efforts clear direction and accountability.
A vague goal like “improve customer experience” won’t cut it. Here are better specific objectives:
- Boosting retention by 15% in six months
- Halving new user time-to-value by Q4
- Increasing satisfaction at critical touchpoints by 20% annually
These specific objectives help you track progress and determine if your journey mapping initiative succeeded. On top of that, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as progress milestones to help you make evidence-based decisions throughout the visualization process.
Note that each mapping project should target one specific goal. Maps that try to tackle multiple objectives at once often become too generic or complex and lose their effectiveness. Your goals will show which parts of the customer experience need the most attention and resources.
Choose the right customer segment
Journey mapping works best when you create it for a specific customer type instead of trying to fit everyone into one map. Unless you run an early-stage company with a single product and customer persona, focus on one customer segment per map.
Let’s identify your ideal customers:
- Who are your existing customers?
- Who makes up your target audience on social media?
- What types of customers do you have in your email lists?
- What problems do these consumers want to solve?
Build detailed customer personas using real data and interviews rather than assumptions. Each persona should show key goals, needs, pain points, and tasks that shape customer behavior. Companies with different audiences might need separate journey maps for each demographic segment.
Start by building maps for your most common customer types or those who buy your most valuable products. This focused approach ensures your visualization offers meaningful insights instead of generic observations that don’t drive action.
Decide on the journey stage to map
Your journey map’s scope plays a big role in how useful it becomes. You’ll need to choose between mapping an end-to-end customer journey or focusing on a specific sub-journey.
Organizations just starting their customer experience initiatives often benefit from end-to-end journey mapping. This detailed approach shows customer movement through awareness, consideration, purchasing, and post-purchase activities. It gives you a complete view to spot areas that need the most attention across the entire customer lifecycle.
A specific sub-journey lets your team head over to particular aspects of the customer experience in detail. End-to-end journeys might cover years, but sub-journeys usually happen over days or weeks. This shorter timeframe lets you capture more detailed information about customer experiences as they happen.
Your first map should start with a known issue, specific persona, or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope manageable by focusing on something you can break into four or five clear steps. This approach makes the mapping process easier while still giving valuable insights.
The right journey scope depends on your specific objectives. This choice involves trade-offs—too broad a journey might not show enough detail for corrective actions, while too narrow a focus could miss important opportunities nearby.
Build Customer Personas and Backstories
Personas are vital to visualizing your customer’s trip. They act as main characters in your mapping story. These detailed representations turn abstract data into relatable human profiles that guide your mapping process.
Use data to create realistic personas
You need more than guesswork and demographics to create powerful personas. In fact, personas based on actual customer behavior provide much more value than made-up characters built on assumptions.
Here’s how to gather information from multiple sources:
- Customer interviews and surveys – Get first-person insights about goals, frustrations, and priorities directly from users
- Website and product analytics – Study behavioral patterns, including popular features, common drop-off points, and usage metrics
- Social media insights – Get into how customers talk about your products and interact with your brand publicly
- Support tickets and reviews – Look through customer feedback to find common themes and pain points
- CRM data – Make use of existing customer information about purchase history and priorities
Combining these different data sources creates a complete picture of each customer group. This method ensures your personas show real behaviors instead of internal assumptions about your audience.
Facebook shows how well this works. The company analyzed user data to create specific personas after receiving anonymous complaints. Their research showed teenagers felt embarrassed about tagged photos, with girls mentioning this problem more often than boys. These findings helped Facebook improve its coverage and support systems based on real user needs.
Each persona should include:
- A name and realistic photo to promote connection
- Demographic information (age, location, education, income)
- Personal attributes (goals, needs, interests)
- Behavioral patterns and priorities
- Technological proficiency and device usage
- Quote or story that captures their viewpoint
Your personas should evolve with time. Markets change constantly, making unchanging personas quickly obsolete. You need systems to update your personas with new data, keeping them accurate representations of current customers.
Understand user motivations and pain points
Demographics provide simple context, but understanding motivations and pain points adds depth and usefulness to your personas. These elements help predict customer behavior throughout their trip.
Look beyond basic goals like “finding a product” when mapping motivations. Find the core needs—customers might want efficiency, status, security, or something completely different. To cite an instance, a car-shopping persona might care about safety, environmental values, or social image, leading to different behaviors.
You can spot pain points through:
- Exit surveys that show why people leave
- Session recordings that reveal moments of frustration
- Customer support conversations highlighting common problems
- Open-ended questions that bring detailed feedback
Document the emotions your personas might feel at each touchpoint in your journey map. A well-crafted persona helps you understand both customer actions and feelings during brand interactions. This emotional mapping shows critical points where satisfaction drops and people might leave.
Note that emotions drive decisions. Understanding a customer’s emotional state at each journey stage helps create experiences that address concerns at the right moment. Research shows that tracking emotions throughout the customer trip helps businesses identify when customers feel frustrated, excited, or confused.
Data-backed personas turn your journey maps from simple flowcharts into detailed stories about real customer experiences. The real value comes when these personas guide your decisions—shaping product development, marketing messages, and support processes based on genuine customer understanding.
Map Out Touchpoints, Emotions, and Actions